Blackrock has been embroiled in controversy for many years now, implicating the world’s largest asset manager in a complex array of issues spanning climate action and investment strategies. As the world’s biggest asset manager led by Larry Fink, BlackRock’s decisions wield unbelievable influence over financial markets and public perception.
If you’re seeking a comprehensive understanding of this multifaceted situation, this article will deliver a detailed exploration of the facts surrounding the BlackRock controversy. Business2Community provides an examination of how investment giants like BlackRock and Vanguard operate within the complexities of the financial markets and the political landscape.
BlackRock Controversy – Key Facts
- The recent controversy began with BlackRock’s investments in sectors criticized for environmental, social, and governance (ESG), particularly fossil fuels, despite CEO Larry Fink’s commitment to addressing climate change and promoting sustainability.
- Activists, environmental organizations, and politicians raised concerns about BlackRock’s voting record on climate resolutions, accusing the firm of failing to align its investment practices with its stated ESG policies.
- The controversy has yet to reach a clear resolution, with ongoing scrutiny from various stakeholders, including lawmakers and the public, with BlackRock still navigating relationships with ESG-focused investors and clients in the fossil fuel industry.
The Story of the BlackRock Controversy
BlackRock has been at the center of numerous controversies, primarily for its investments in sectors criticized for environmental, social, and governance (ESG) issues. These controversies have challenged the company’s public and corporate reputation, impacting how it is perceived globally.

What is BlackRock?
BlackRock is an American multinational investment management corporation, renowned as the global investment giant with significant stakes in various companies and sectors.
Founded in 1988, BlackRock provides a wide range of services including mutual funds, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), risk management, and advisory services for institutional and individual investors.
Headquartered in New York City, BlackRock has offices in over 30 countries and clients in more than 100 countries.
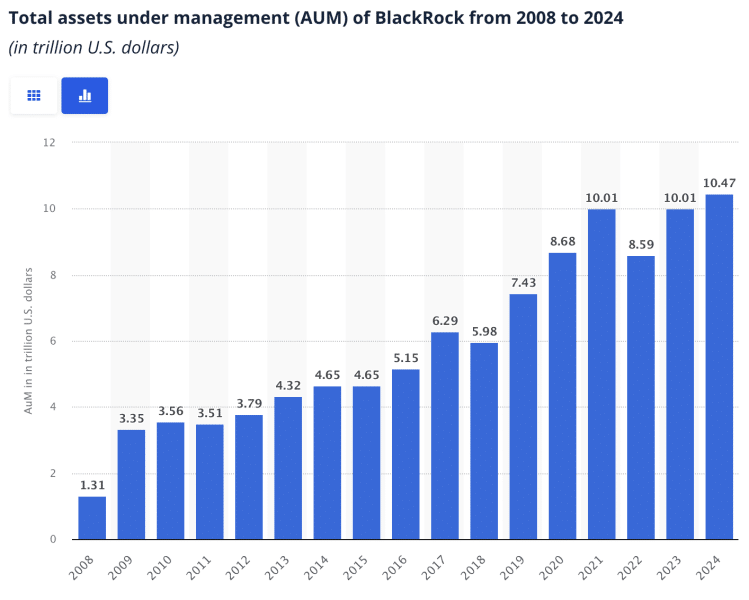
With over $10 trillion in assets under management, BlackRock plays a pivotal role in the financial industry, controlling global markets through its investment decisions and stewardship.
The company is known for its technological advancements in investment management, particularly with its Aladdin platform, which offers a mix of technology and asset management services.
Despite its achievements, BlackRock’s significant impact on global markets inevitably attracts both scrutiny and debate, often making it a focal point for discussions about corporate governance, environmental responsibility, and economic influence.
BlackRock’s Policy on Climate Change in 2020
In 2020, BlackRock, under CEO Larry Fink’s leadership, publicly declared climate change to be a critical long-term issue, emphasizing the need for companies to address environmental sustainability.
Fink claimed BlackRock’s $10 trillion assets could address climate change while still being profitable.
BlackRock’s website states the following:
In January 2020, BlackRock committed to putting sustainability at the center of our investment process, based on the conviction that integrating sustainability-related information into the investment process can help our portfolio managers manage risk and make better informed investment decisions.
Media outlets like The New York Times, CNBC, and Bloomberg praised BlackRock’s supposed environmental commitment at the time.
The portrayal of Fink and BlackRock suggested a significant cultural shift in Corporate America, moving from pure profit motives toward more responsible environmental stewardship. However, despite these strong public commitments, BlackRock’s actual voting behavior on shareholder resolutions in companies it has an interest in concerning climate risk reflected a different reality.
Its policy during this time revealed a major disconnect between rhetoric and action as it continued to resist backing significant climate-related proposals. Because BlackRock has so much control over so many companies, this lack of action has likely had a tremendous impact, weakening the global fight against climate change.
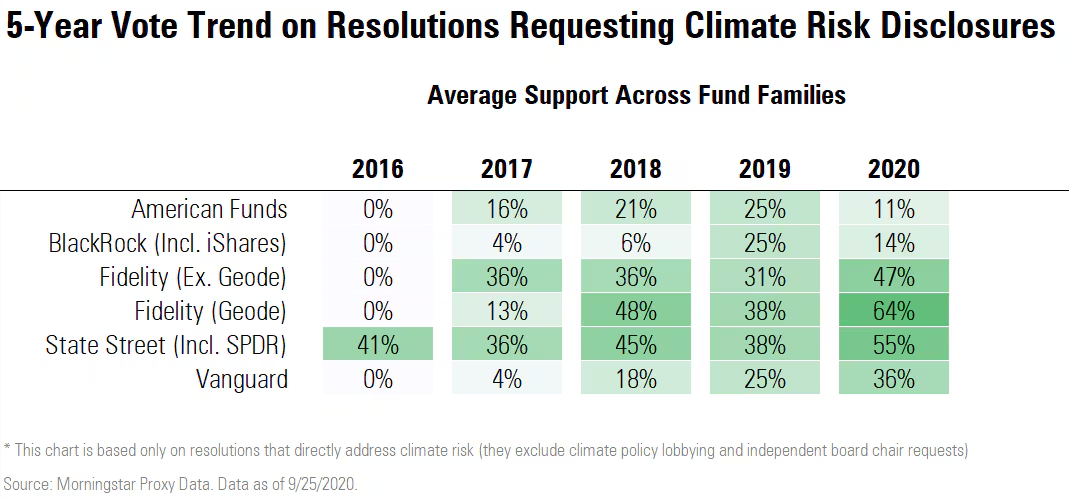
BlackRock’s Voting Record on Climate Resolutions
BlackRock’s voting record on climate change resolutions was notably poor in 2020, the same year it had declared a shift in rhetoric.
Competitors such as Vanguard, State Street, and Fidelity increased their support for shareholder resolutions on climate change, while BlackRock voted against more than 80% of such proposals.
Support for climate-related disclosure resolutions declined at BlackRock from 25% in 2019 to 14% in 2020.
Despite acknowledging the importance of addressing climate change, BlackRock’s support for climate-related resolutions remained notably low. Fewer climate-risk-focused resolutions were brought to vote in 2020, partly due to companies engaging more with investors to avoid resolutions.
The SEC’s growing opposition to climate-related proposals discouraged shareholders from filing resolutions. Even so, BlackRock ranked last in support among major investment firms for a broader set of climate-related resolutions. Remember that Blackrock has more control over large American companies than almost any other business or entity so its lack of support for climate policies is extremely impactful.
The firm opposed all but two of the 12 key climate-linked resolutions flagged by the Climate Action 100+ coalition.
BlackRock’s ESG funds voted against significant climate-related resolutions that could have garnered majority support.
Contradictions in Climate Policy
By 2022, Fink had distanced himself from “woke” capitalism, supporting fewer climate resolutions and partnering with fossil fuel companies.
In early 2022, it was revealed by the Bureau for Investigative Journalism that BlackRock’s executives had privately reassured Texas regulators of their support for the oil and gas industry, contradicting CEO Larry Fink’s earlier climate pledges.
An email from Texas’s oil regulator noted that BlackRock’s leadership no longer seemed to believe their public stance on the fossil fuel sector. Critics argue that BlackRock never really supported climate efforts and just wanted to appease consumers, voters, and politicians with a shift in rhetoric.
Pressure from several US states, responsible for over $600 billion in funds, prompted financial institutions to downplay their environmental commitments.
States like Texas enacted laws requiring banks to certify they do not boycott energy companies to maintain business relationships. This situation forced institutions to choose between climate commitments and potentially lucrative business opportunities.
BlackRock continued to navigate this complex landscape, trying to appease both ESG-focused investors and clients in the fossil fuel industry.
Yet, despite their efforts, skepticism persisted, particularly from states like West Virginia that are reliant on fossil fuel industries. They expressed concern over BlackRock’s alleged support for net-zero strategies that could undermine fossil fuel industries, despite the worsening climate crisis.
BlackRock’s Crypto Investments
In December 2023, Fink announced that BlackRock would invest heavily in cryptocurrencies, notably Bitcoin, thereby revitalizing interest in fossil fuel-dependent industries. This shift raises critical concerns given the significant carbon footprint associated with cryptocurrency mining.
A UN University study highlighted that if Bitcoin were a country, its energy consumption would rank 27th globally, with its emissions comparable to burning 84 billion pounds of coal.
Fink’s pivot towards crypto and away from climate policies contradict his earlier claims of fostering responsible capitalism and addressing climate change. This inconsistency should prompt the media to approach corporate claims of sustainability with skepticism, recognizing that the pursuit of short-term profits often overshadows genuine environmental commitments. And this shouldn’t be surprising.
Incentives for executives are always centered around profit and growth and reasonable pro-climate policies would hurt the bottom lines of many large corporations in the short term. The disastrous consequences of climate change will cost businesses and regular people drastically more in the long term but executives, shareholders, and asset managers don’t seem to care.
BlackRock’s actions underscore the need for stricter scrutiny of corporate environmental policies and the demand for accountability beyond mere rhetoric.
Despite its vocal support for sustainability, BlackRock maintains large holdings in companies with poor environmental records, including major oil and gas corporations.
Influence on Global Politics and Economy
The reach of BlackRock’s influence extends beyond conventional financial realms, manifesting in unexpected spheres such as internet-fueled conspiracy theories.
In July 2024, BlackRock became a focal point of controversy after a fleeting connection between would-be Trump assassin Thomas Matthew Crooks and the company surfaced.
This connection, although tenuous and seemingly innocuous — Crooks merely appeared briefly in a promotional video — became the basis for online rumors suggesting BlackRock’s involvement in the incident and various unsubstantiated claims about its overarching power.
The massive viewership and rampant speculation surrounding these events underscore prevailing suspicions and misconceptions about BlackRock’s role in global affairs. These conspiracy theories thrive on BlackRock’s significant financial involvement across numerous sectors, with detractors misinterpreting strategic investments as efforts to control world affairs. These conspiracy theories also often devolve into various versions of the antisemitic great replacement theory.
While these conspiracies are unfounded, there is no doubt that BlackRock has tremendous control over countless US businesses and that it has used that power to fight climate change efforts (despite its antithetical rhetoric). These narratives reflect widespread concerns about the concentration of financial power, illustrating how BlackRock’s sheer size, power, and secrecy invoke both wonder and paranoia in equal measure.
Investments in Chinese Companies
In 2023, critics raised alarms over BlackRock’s expanding investments in China, particularly in companies linked to human rights abuses and the Chinese Communist Party, notably in surveillance technology.
Scrutiny from a Congressional select committee spotlighted significant ethical and security concerns regarding BlackRock’s investment strategies, especially its ties to Chinese companies on US government blacklists. The inquiry questioned whether American savings managed by BlackRock and MSCI were inadvertently funding entities developing military technologies for the People’s Liberation Army or those involved in human rights violations.
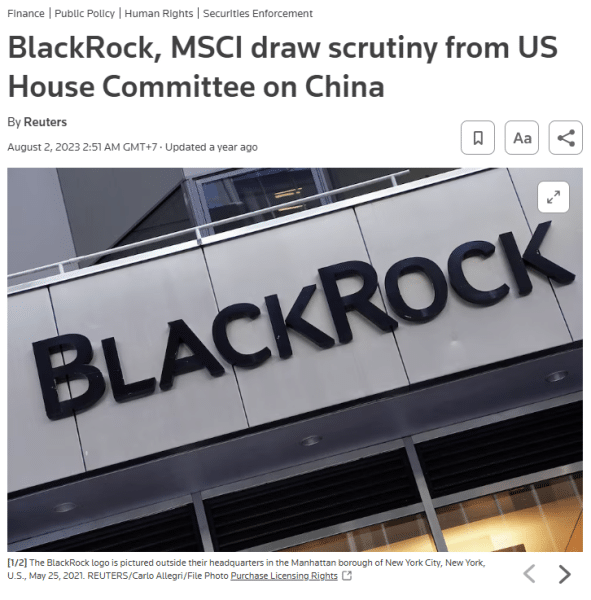
Findings revealed that BlackRock invested over $429 million in these controversial companies through various funds, potentially posing national security risks and conflicting with American values.
This situation brought to the forefront a critical dilemma for institutional investors: how to balance fiduciary responsibilities with the need to protect national interests. While BlackRock acknowledged its substantial index fund presence in China, it asserted compliance with US laws and commitment to cooperating with the committee’s inquiries.
This complex scenario raised important questions about investing in emerging markets with known regulatory and ethical challenges, emphasizing the need for greater transparency and accountability from asset managers to protect American interests.
Pandemic Response and Corporate Bailouts
BlackRock’s involvement in the Federal Reserve’s COVID-19 bailout schemes has sparked debate and concern among US lawmakers across the political spectrum.
As the asset manager charged with implementing a groundbreaking program to purchase hundreds of billions of dollars in corporate debt, BlackRock has found itself at the heart of controversial issues regarding its monumental influence and potential conflicts of interest.
In particular, its ability to affect the bond markets where it’s engaged with the Fed’s intervention has been scrutinized.
Representative Chuy García highlighted the need for stringent oversight, emphasizing that BlackRock operates without the same regulatory constraints as traditional banks, which leaves room for potential threats to transparency and fairness within the market.

The firm maintained that its role, governed and directed by the Fed, is strictly in accordance with detailed guidelines meant to support credit access for US companies. Yet, concerns about BlackRock’s overall influence and its dual objectives of serving governmental interests while maintaining its vast private investments have led to bipartisan calls for more comprehensive oversight.
Notably, its increasing clout within Washington and financial markets echoes earlier financial giants’ intricate entanglements with government, suggesting a need for vigilance against further cementing of BlackRock’s structural importance in the global economy.
The dynamics of BlackRock’s relationship with the US government during the pandemic serve as a potent reminder of the delicate balance required between leveraging private sector expertise and safeguarding public interest.
The Consequences of the BlackRock Controversy
The BlackRock controversy has had far-reaching consequences across various sectors, impacting investors, policymakers, and the public’s perception of corporate responsibility. Criticism of BlackRock CEO Larry Fink’s strategies intensified as environmental activists and concerned citizens condemned the firm for its continued investments in fossil fuels.
The disconnect between BlackRock’s ESG policies and its actual voting record on climate resolutions has left many questioning the integrity of the firm’s commitment to sustainability.
Politicians from states like Texas, which rely heavily on public energy companies, have sought to hold BlackRock accountable, pushing bills that require transparency regarding investments in energy sectors. BlackRock even lost its contract with the state of West Virginia because of the company’s (stated) policy on net zero emissions.
This backlash has prompted BlackRock to navigate a complex landscape where it must balance its obligations to shareholders with public pressure to act responsibly. The significant amount of capital BlackRock invests in companies with questionable environmental records has led to a rising chorus of voices calling for greater scrutiny of Wall Street’s practices.
The scrutiny has also spurred conspiracy theories linking BlackRock to global power dynamics, especially following the first 2024 assassination attempt on Donald Trump that saw a fleeting connection to the firm. These narratives, while largely unfounded, reflect widespread anxiety about the concentration of financial power in the hands of a few asset managers, underscoring the need for accountability.
As BlackRock continues to face pressure from multiple fronts, the implications for its future operations and reputation remain uncertain. The backlash highlights the challenges faced by investment giants as they grapple with the dual objectives of profitability and social responsibility.
What Can We Learn From the BlackRock Controversy?
The BlackRock controversy serves as a crucial lesson for business leaders navigating the intersection of finance and social responsibility. The need for transparency in investment practices is paramount, especially for firms that claim to prioritize sustainability while investing heavily in fossil fuels.
Understanding the complexities of ESG investing and the climate change fight in general is essential. Businesses should recognize that public commitments to climate action must align with actual practices and voting records. This alignment is critical in maintaining trust among investors and the public, particularly in an era where the climate crisis looms large.
The situation emphasizes the importance of being aware of how public perception can shape business strategies. Investment firms must consider the impact of their decisions on society and the environment, especially as consumers become increasingly conscientious about where they invest their money.
Ultimately, the BlackRock case reminds us that the financial world is interconnected with broader societal issues. Leaders should prioritize ethical investing, not only for compliance but to cultivate a more sustainable and responsible business environment. Balancing profit with purpose is not merely a trend; it’s a necessary approach for the future of business in a rapidly changing world.