Human behavior affects organizational growth. In this article, we are going to talk about what I’ve learned about how emotions affect human behavior.
There are different types of emotions that can influence the way we live and talk to others.
Sometimes, it may seem like these emotions rule us. The actions we take, the choices we make and the perceptions we have been influenced by greatly impact our emotions at any given moment.
Psychologists and scholars from other fields have identified the different types of emotions we experience as humans. Different theories have come up to categorize and explain different types of emotions that people have.
Understanding the 6 Different Types of Emotions
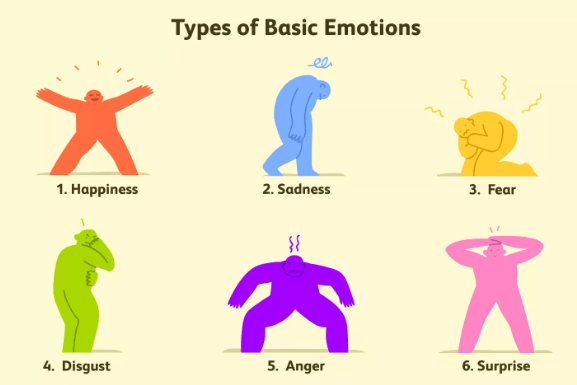
There are six basic emotions that are universally experienced in all people irrespective of their cultures.
These emotions are:
- Sadness;
- Happiness;
- Disgust;
- Surprise;
- Fear;
- Anger.
If we try to go further and expand these emotions, we will come up with other emotions such as shame, pride, excitement and embarrassment.
Combining Different Emotions
Emotions can be joined together to form different feelings.
Just like the way we can mix different colors to form different shades. The basic emotions discussed above act like building blocks. Mixed emotions build complex emotions.
For example, basic emotions such as trust and joy can be combined to create a greater emotion such as love.
Now we will take a closer look at some of the basic emotions and try to figure out how they affect human behavior in an organization.
1. Happiness
Most people strive to have the happiness of all the types of emotions discussed above.
Happiness is a pleasant emotional state, and it is characterized by the feeling of joy, contentment, satisfaction, gratification, and well-being. Scholars have done numerous researches on happiness since the 1960s within different disciplines such as positive psychology.
Happiness is sometimes expressed through body language, facial expressions such as smiling, and a pleasant tone.
Happiness is one of the basic emotions, but things that create happiness are majorly influenced by culture.
For example, the hip-hop culture emphasizes that buying things such as flashy cars makes one happy. This makes it hard to understand the things that contribute to happiness because different people are influenced by different things.
Some people believe that health and happiness are connected.
According to research, happiness plays a major role in mental and physical health. We can link happiness to a variety of outcomes such as increased marital satisfaction, increased salaries and a welcoming working environment when it comes to organizations.
Conversely, we can link unhappiness to a variety of things such as anxiety, stress, loneliness, depression and more.
Key indicators of happiness:
- Body language: Open posture, relaxed demeanor.
- Physical reactions: Increased energy, a sense of lightness.
- Facial expressions: Smiling, bright eyes, relaxed facial muscles.
2. Sadness
Sadness is a transient emotional state.
It is typically characterized by feelings of grief, disappointment, disinterest, hopelessness, and a dampened mood.
Sadness is an emotion that all people experience. In some cases, people experience severe and prolonged periods of sadness that can become depression.
There are several ways we can express sadness such as quietness, dampened mood, withdrawal from others, lethargy and crying.
The severity and type of sadness can vary depending on the cause and people cope with sadness in different ways. Sadness can make people avoid other people or even have negative thoughts about life.
Key indicators of sadness:
- Body language: Slumped posture, slow movements.
- Physical reactions: Tears, a feeling of heaviness.
- Facial expressions: Frowning, downturned mouth, teary eyes.
3. Fear
This is a very powerful emotion, and it can play an important role in survival.
People go through flight or fight response when they face some sort of fear. Your heart rate increases, your muscles become tense, and your mind becomes more alert. This primes your body either to stand and fight or to run from danger.
The response ensures that you are prepared to deal with the threats in your environment which can be an organizational setting.
Expressions of fear include attempts to flee or hide from threats, facial expressions such as pulling back the chin or widening the eyes and physiological reactions such as increased heart rate.
People experience fear in different ways. Some people may be more sensitive to certain objects that may trigger fear. Fear can be defined as an emotional response to a sudden threat.
Key indicators of fear:
- Body language: Tense posture, possibly shaking.
- Physical reactions: Increased heart rate, sweating, trembling.
- Facial expressions: Wide eyes, raised eyebrows, open mouth.
4. Disgust
This is a basic emotion that can be displayed in numerous ways such as turning away from things of disgust, facial expressions such as curling the upper lip and wrinkling the nose and physical reactions such as retching or vomiting.
Different things can cause disgust such as unpleasant smell, sight or taste.
Experts believe that disgust evolved as a reaction to harmful foods. When people taste or smell foods that have been contaminated, they experience disgust. Infection, poor hygiene, rot, blood, and death can cause disgust.
There is also moral disgust when people observe other people engaging in behaviors that they find immoral, distasteful or evil. Relationships between bosses and employees in organizations can be disgusting to other employees.
Key indicators of disgust:
- Body language: Turning away, withdrawing.
- Physical reactions: Gagging, feeling of nausea.
- Facial expressions: Wrinkled nose, curled lip.
5. Anger
This is a very powerful emotion, and it is characterized by feelings of agitation, hostility, antagonism, and frustration towards others.
Anger is similar to fear in that it can trigger a flight or fight response in the body. A threat can generate a feeling of anger and make you fend off the danger or fight to protect yourself.
Anger can be displayed through body language such as turning away from someone, facial expressions such as glaring or frowning, tone of voice such as yelling or speaking gruffly, a physiological response such as turning red or sweating, and aggression such as kicking, hitting or throwing objects.
Anger can negatively affect the productivity of employees in an organization.
Key indicators of anger:
- Body language: Clenched fists, tense posture, invasion of personal space.
- Physical reactions: Reddening of the face, increased heart rate.
- Facial expressions: Frowning, glaring, tight jaw.
6. Surprise
This is another one of the basic types of human emotions.
It is typically brief, and we can characterize surprise by a physiological startle response due to unexpected things. Surprise can be negative, positive or neutral. The unpleasant surprise might involve someone scaring you as you walk.
An example of a pleasant surprise is when you arrive home and find your friends gathered to celebrate your birthday. We can characterize surprise by facial expressions such as widening the eyes raising the brows and opening the mouth.
We can also describe surprise through physical responses such as jumping up or back and verbal reactions such as gasping, screaming and yelling.
Positive surprises to employees in an organization can increase their productivity.
Key indicators of surprise:
- Body language: Sudden backward movement or freezing in place.
- Physical reactions: Quick intake of breath, elevated heart rate.
- Facial expressions: Wide eyes, raised eyebrows, open mouth.
Other Types of Emotions
Beyond the six basic emotions of sadness, happiness, disgust, surprise, fear, and anger, there are numerous other emotions that humans experience. These include:
- Love: A complex mix of affection, warmth, and attachment often associated with strong interpersonal relationships.
- Jealousy: A response to perceived threats to a valued relationship or to one’s self-esteem.
- Guilt: A feeling of responsibility or remorse for some offense, crime, wrong, whether real or imagined.
- Shame: A painful emotion caused by consciousness of guilt, shortcoming, or impropriety.
- Pride: A feeling of self-respect and personal worth, often related to personal achievements or qualities.
- Curiosity: A strong desire to know or learn something, driving exploration and learning.
- Boredom: A state of feeling disinterested or unengaged with one’s surroundings or activities.
- Empathy: The ability to understand and share the feelings of another, fostering social connections.
Other Theories of Emotion
Several theories have been proposed to understand and categorize human emotions:
- James-Lange Theory: Suggests that emotions occur as a result of physiological reactions to events.
- Cannon-Bard Theory: Argues that we feel emotions and experience physiological reactions simultaneously.
- Schachter-Singer Theory: Also known as the two-factor theory, it posits that emotion is based on physiological arousal and cognitive label.
- Cognitive Appraisal Theory: Suggests that personal interpretation of a situation is the key to emotional experience.
- Facial Feedback Theory: Implies that facial expressions are capable of influencing our emotions.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the different types of emotions is crucial in comprehending human behavior, especially in organizational contexts.
Recognizing these emotions and their impacts not only enhances interpersonal relationships but also contributes to personal and professional growth.
Embracing this diversity of emotions leads to a more empathetic and effective environment, whether in personal life or within an organization.